food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome in adults
The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy that affects the gastrointestinal GI tract.
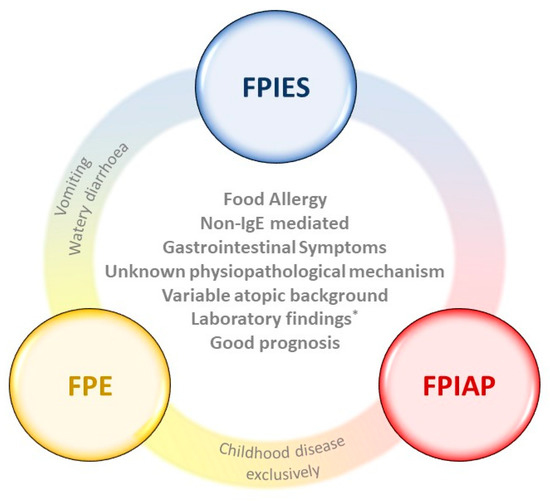
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare non-immunoglobulin E-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy primarily diagnosed in infancy but has also been reported in older children and adults.

. FPIES prevalence which still needs to be accurately determine in different populations appears to be higher than previously thought ie up to 07 in infants in the 1st year of life. Food protein-induced enterocolitis-like syndrome in a population of adolescents and adults caused by seafood J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. Food proteininduced enterocolitis-like syndrome in a population of adolescents and adults caused by seafood.
FPIES presents in two different forms. Unlike most food allergies symptoms of FPIES do not begin immediately after eating. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition that occurs in infants and young children although it can rarely affect older children or adults as well.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergic disorder that has gained a major interest the past decade. Epub 2012 Jul 24.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to weight loss failure to thrive dehydration and metabolic. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food protein.
Although food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES a non-mediated food allergy with symptoms of repetitive vomiting diarrhea lethargy hypotonia hypothermia hypotension and. Ad Find Deals on inflammatory bowel disease supplement in Nutrition on Amazon. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES in adults is being increasingly recognized.
Many allergists report that symptoms suggestive of FPIES are on occasion reported by adult patients and mainly refer to ingestion of seafood. Egg provoked food proteininduced enterocolitislike syndrome in an adult. Adult Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome 1 Division of Immunology Allergy and Retrovirology Department of Pediatrics Texas Childrens Hospital Baylor.
Adults with possible food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome with crustacean ingestion. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is increasingly recognized in adults with a predominance in women. Vomiting is often followed by a paleness to the skin.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system.
It typically causes vomiting and bloody diarrhea after consumption of certain foods the trigger foods arent the same for everyone. Instead it can take hours before severe symptoms begin. Acute FPIES reactions typically present with delayed repetitive vomiting lethargy and pallor within 1 to 4 hours of food ingestion.
Shearer Center for Human Immunobiology Texas Childrens Hospital Houston TX United States 3 Division of Allergy and. Severe reactions can prompt a medical emergency such as. PDF Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children.
Adults with possible food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome with crustacean ingestion Abstract. Find read and cite all the research. Differences in clinical manifestations trigger foods and prognosis compared to pediatric FPIES have been reported.
In recent years new-onset adult FPIES has been recognized. The underlying pathogenic mechanism of FPIES has yet to be elucidated thus disease-specific dia. To describe the clinical characteristics prognosis and associated factors in adult FPIES.
An acute form and a chronic form. However little is known about its characteristics. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults.
Most of the reactions were due to seafood mollusks crustaceans and fish and egg but other foods like peanut almond mushroom corn chicken and duck were also implicated. Bryan N Fernandes Robert J Boyle Claudia Gore Angela Simpson Adnan Custovic. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

International Fpies Association Facebook

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
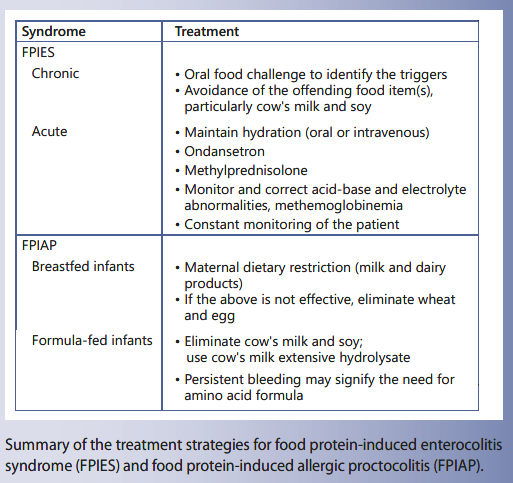
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
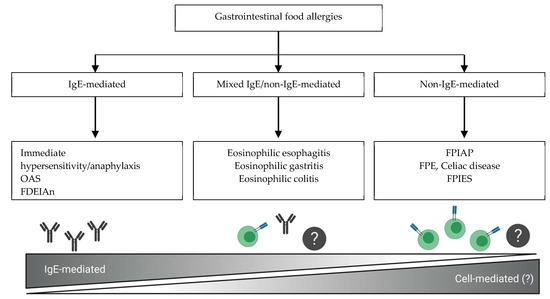
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Caubet 2019 Clinical Amp Experimental Allergy Wiley Online Library

International Fpies Association Facebook

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

International Consensus Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Executive Summary Workgroup Report Of The Adverse Reactions To Foods Committee American Academy Of Allergy Asthma Immunology Journal
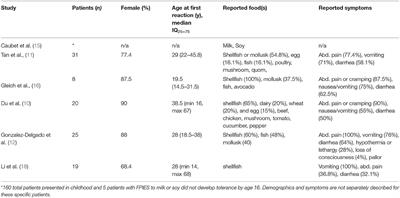
Frontiers Adult Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Fpies In Babies Symptoms Risk Factors And More

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Advances In Understanding Immune Mechanisms Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
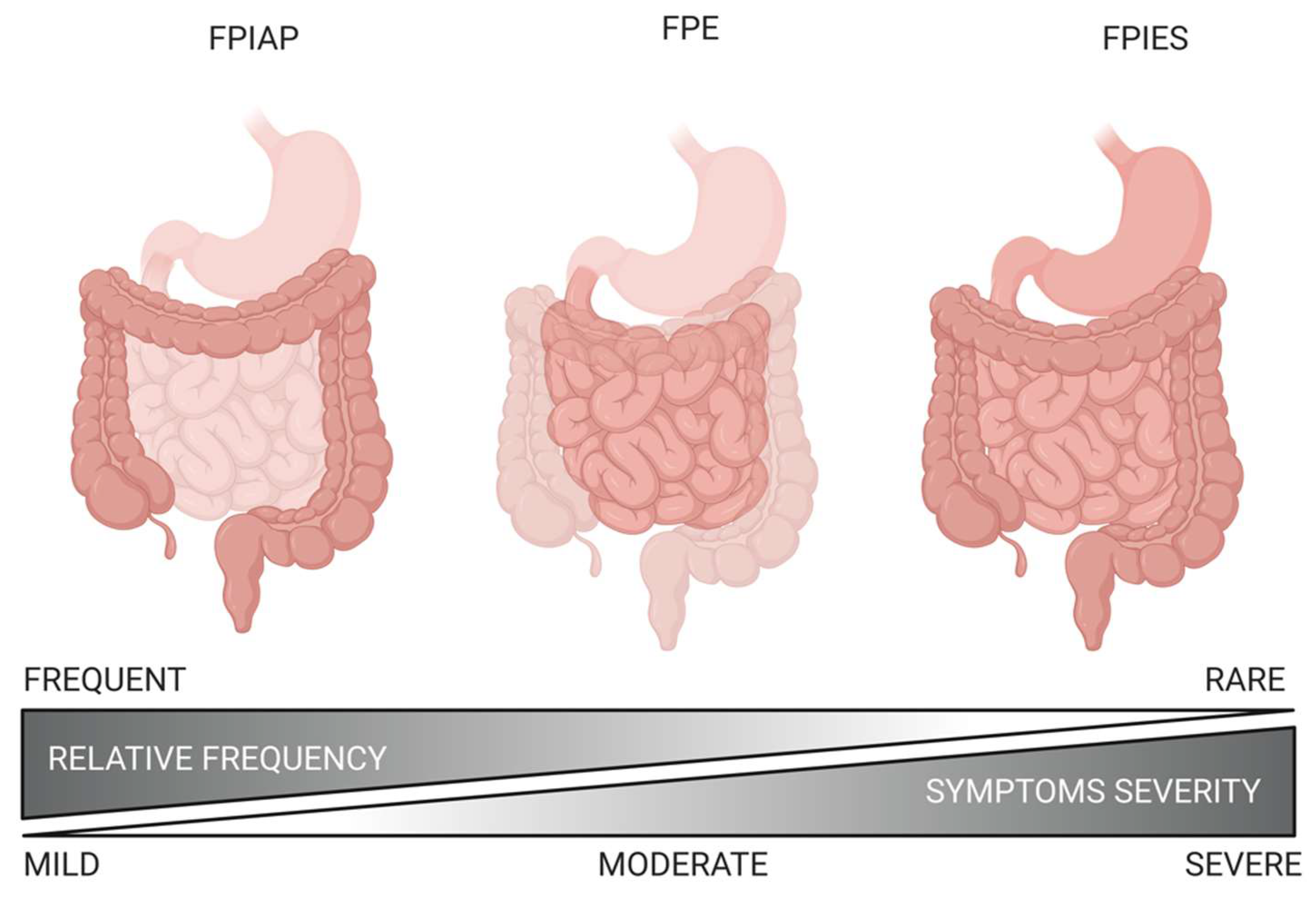
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html